Siberia
2009-08-25 17:08 BJTSpecial Report: Asia Pacific |
Profile of Siberia
Siberia is the name given to the vast region constituting almost all of Northern Asia and for the most part currently serving as the massive central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, having served in the same capacity previously for the USSR from its beginning, and the Russian Empire beginning in the 16th century.
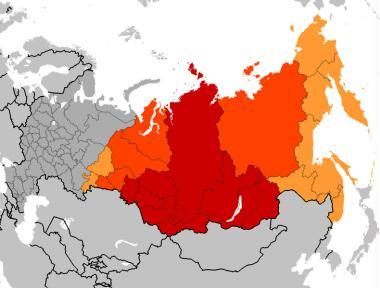 |
Geographically, it includes a large part of the Eurasian Steppe and extends eastward from the Ural Mountains to the watershed between Pacific and Arctic drainage basins, and southward from the Arctic Ocean to the hills of north-central Kazakhstan and the national borders of both Mongolia and China. It makes up about 77% of Russia's territory (13.1 million square kilometres), but only 25% of Russia's population (36 million people).
Geography and geology
With an area of 13.1 million km² (5.1 million square miles), Siberia makes up roughly 77% of the total area of Russia. Major geographical zones include the West Siberian Plain and the Central Siberian Plateau. Siberia covers almost 10% of Earth's land surface (14,894,000 km²).

 Mail
Mail Share
Share Print
Print


 Video
Video









 2009 China Central Television. All Rights Reserved
2009 China Central Television. All Rights Reserved